- Dark matter only simulations were performed using 768^3, 1576^3, 3072^3 and 6144^3 particles.
- Magneto-hydodynamical, non radiative simulations but following also a cosmic ray component using 2x3072^3 gas and dark matter particles.
- Hydrodynamical, full galaxy formation physics simulation (same as Magneticum) using 2x768^3, 2x1576^3 and 2x3072^3 gas and dark matter particles (last one only down to z = 2).



With the aim to study in detail the interaction of galaxies with the ICM as well as microphysical processes like the evolution of magnetic fields, turbulence and cosmic rays within the ICM we extending the Dianoga simulations to far higher resolution. The aim is have 250 time more (Phase I) and 2500 times more (Phase II) resolution elements. This pushes simulations of massive clusters to so far never reached precision. Dark matter particle masses in the simulations will be 3.3e6 Msol/h (250x) / 3.3e5 Msol/h (2500x) and softening for dark matter and gas particles will be 0.5 kpc/h (250x), 0.2 kpc/h (2500x). The clusters will therefore be described by more than 600,000,000 particles within the virial radius and typically the simulations will resolve 100,000 galaxies within individual clusters.
With the aim to study in detail the evolution of galaxies and especially the outskirts of the galactic halo, we extending the Dianoga simulations to include groups, massive field galaxies and normal galaxies to be simulated at very high resolution. The aim is to have 250 and 2500 time more resolution (Phase I) and even explore 25000 times more resolution (Phase II). This pushes simulations of galaxies to have dark matter particle masses of 3.3e4 Msol/h (25000x). A MW like galaxy will be therefore resolved with 20,000,000 particles within the virial radius.
The project wiki (restricted).
| Magneticum Pathfinder | |
|
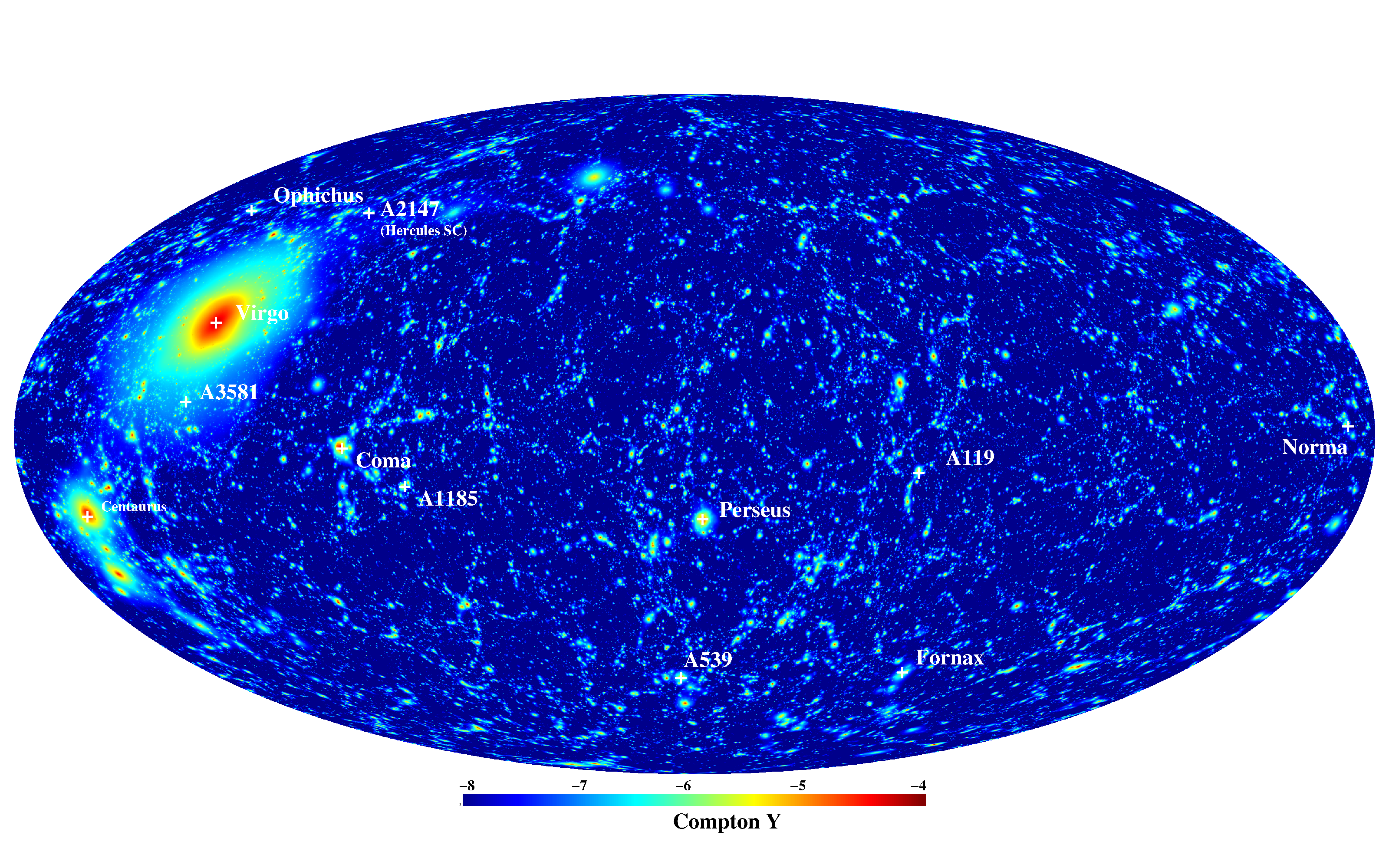
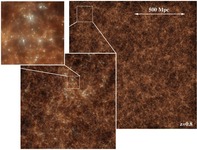
Magneticum Pathfinder aims to follow the formation of cosmological structures in a so far unaccomplished level of detail by performing a set of large scale and high resolution simulations, taking into account many physical processes to allow detailed comparison to a variety of multi-wavelength observational data. Using WMAP7 cosmology, the largest sets of simulations will be Box1 (L=896 Mpc/h, n=2x1526^3, m_dm=1.6e10 Msol/h) and Box2 (L=352 Mpc/h, n=2x1584^3, m_dm=8.3e8 Msol/h) and Box3 (L=128 Mpc/h, n=2x1526^3, m_dm=4.4e7 Msol/h) and various simulations with less particles. All simulations include various physical processes (thermal conduction, star-formation and chemical enrichment, growth of BHs and AGN feedback). First simulations where performed at SARA under the project MagPath. Additional simulations where performed on JUGENE within the framework of a GAUSS proposal. The next larger simulations are performed on SuperMuc within a new GAUSS proposal. The project wiki (restricted). |
| Dianoga | |
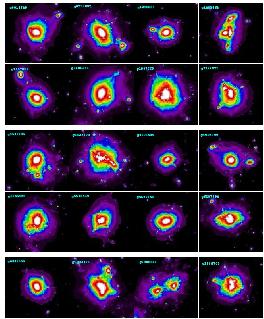 |
Dianoga is a set of mass limited galaxy clusters, extracted
from a low- resolution dark matter (DM) simulation, which covers a box size of 1 Gpc/h and
used 1024^3 particles to describe a standard WMAP-7 LCDM cosmological model. From this simulation we extracted 24
Lagrangian regions around the most massive clusters. For each of these regions, initial conditions have been re-generated
by increasing mass resolution and adding high-frequency modes, while progressively degrading resolution in outer
regions. For each cluster, initial conditions have been generated at two different resolutions: a low resolution (LR)
version, corresponding to a mass of the DM particle in the high-resolution region of 10^9 Msun/h, and a high resolution
(HR) version with 10 times smaller DM particles mass, 10^8 Msun/h.
The projekt wiki (restricted).
Name explanation Dianoga. |
| High resolution Cluster set | |
 |
Hutt is a set of 9 high resolution re-simulations of galaxy
clusters taken from a large size cosmological simulation using the ZIC technique.
In total there are 19 Haloes with masses larger than 0.5e14 Msol/h, of which 4
have masses above 1.0e15 Msol/h. The initial conditions where created to have a
large (typical 5 R_vir) region around the objects, which is free from boundary
effects. These simulations are performed for various combination of physical
effects included. There are several online services available.
Name explanation Hutt. |
| Large filament Simulation | |
 |
Leia is a on high resolution re-simulations of a super
clusters like filament taken from a large size cosmological simulation, spawning
between 4 very missive galaxy clusters, using the ZIC technique.
In total there are 49 Haloes with masses larger than 0.5e14 Msol/h, of which 4
have masses above 5.0e14 Msol/h. The simulation roughly spawns a cylinder of length 60Mpc/h
with a width of 30 Mpc/h. The initial conditions where created to have a
large (typical 5 R_vir) region around the objects, which is free from boundary
effects. These simulations are performed for some combination of physical
effects included. There are several online services available.
Name explanation Leia. |
| Ultra high resolution 12kev Cluster | |
 |
Luke is a ultra high resolution re-simulations of the g8 cluster from
the Hutt sample. Sofar, only the dark matter only run is finished. It has a mass
resolution of 2.0e8 Msol/h for the dark matter particles, and host nearly 11 Million dark
matter particles within R_vir at z=0. A run with cooling, starformation and feedback is actually
running (also including chemical enrichment from SN-Ia and II, by
using the Metget developement by Tornatore et al. (2004)), and a gas run with low viscosity will be started soon.
Name explanation Luke. |
| Very advanced Cluster simulations | |
 |
Vader is a ultra high resolution re-simulations of some clusters from
the Hutt sample. Sofar, starting with g676, the highest mass resolution reached
is 1.0e7 Msol/h for the dark matter particles, corresponding to a gravitational softening of
1 kpc/h, and therefore complements Luke in the small mass end.
Name explanation Vader. |
| Multi Million Particle Keyproject Cluster re-simulations | |
 |
Tarkin is a
set of high-resolution resimulations of clusters extracted
from the cosmological box simulated with the Keyproject-2003, with
initial conditions realized with the ZIC technique. The simulations have
been realized with the twofold aim of reaching high resolution to study
numerical convergence of X-ray and optical observational properties of
galaxy clusters, and to span a variety of models for star formation,
chemical enrichment and feedback strength. The highest resolution runs
resolve each cluster with about 2e6 DM particles within the virial
radius at z=0. They are realized with the original P-Gadget2 code. A
battery of simulations with lower mass resolution (by a factor 3-4) are
realized by also including chemical enrichment from SN-Ia and II, by
using the Metget developement by Tornatore et al. (2004). Different runs
have been carried out by changing the stellar IMF and the wind velocity,
as defined in the original model by Springel & Hernquist (2003). Heavely
suppressed thermal conduction (1/20th Spitzer) is also included,
following the method by Jubelgas et al. (2004)
Name explanation Tarkin. |
| Padova Dark energy Model cluster | |
 |
Padme is a set of 10 re-simulations of galaxy
clusters taken from a large size cosmological simulation using the ZIC technique. In total
there are 17 Haloes with masses larger than 2.0e14 Msol/h. These clusters where re-simulated
within 8 different cosmological models using dark matter only. These cosmology also include
models, where the equation of state of the dark energy depends varies with time. Recently these simulations have
beed extended to also cover some hydrodynamical, cosmological boxes (L=300 Mpc/h, n=2x768^3, m_dm=4.4e9 Msol/h)
simulated using various dark enery models. The cosmological box simulations where
performed at HRLB2 at LRZ under the project h0073.
The project wiki (restricted).
Name explanation Padme. |
| Cosmological, 480^3 Particle Simulation | |
 |
C3PO is a cosmological hydrodynamical simulation of a
representative volume of the Universe, with high enough resolution to
describe in detail the X-ray and Sunyaev-Zeldovich (SZ) properties of
the baryonic intergalactic medium in groups and clusters of galaxies
and within large-scale filaments. The Simulated a box is 192 Mpc/h
on a side and includes the effect of
radiative cooling, cooling/heating by a uniform evolving UV
background, star formation, a recipe to account for the multi-phase
nature of the inter-stellar medium, where star formation takes place,
feedback and metal enrichment from type-II supernova explosions and
the effect of galactic winds.
Name explanation C3PO. |
| Constrained Local Universe including Magnetic Fields | |
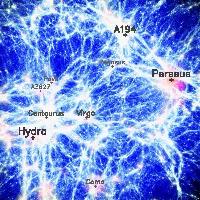 |
Coruscant is a cosmological re-simulation of the local universe
based on initial conditions reconstructed from the 1.2 muJ IRAS full sky survey. This simulation
is designed to represent the observed local neighborhood out to 80Mpc/h and makes it possible
to identify prominent haloes from the simulations with real observed galaxy cluster. This re-simulation
also includes adiabatic gas physics and the evolution of a week, seed magnetic field. Its purpose
is to study the magnetic field and the propagation of cosmic rays within clusters and the local universe.
Recently there have beed also re-simulations to study the distribution and evolution of magnetic fields
originating from galactic outflows. The
project Wiki (restricted).
Name explanation Coruscant. |
| Constrained Simulation for detectabiliy of WHIM in the Local Universe | |
 |
Salacious
is a cosmological re-simulation of the local universe
based on initial conditions reconstructed from the 1.2
muJ IRAS full sky survey. This simulation
is designed to represent the observed local neighborhood
out to 80Mpc/h and makes it possible to identify prominent
haloes from the simulations with real observed galaxy cluster.
This re-simulation is similat to the Coruscant simulation,
but instead of tracing the magnetic field it follows cooling,
starformation, feedback and the spreading of metal in the intra
cluster medium. The main goal of this simulation is to study
the detectability of WHIM in local super cluster structures.
Recently it was also re-simulated including the growth of BHs and
the feedback by AGNs.
Name explanation Salacious. |
| Lando | |
 |
Lando consist of two cosmological simulations.
Box 1 (L=500 Mpc, n=800^3, m_dm=2.0e10 Msol/h) and Box2 (L=1200 Mpc/h, n=960^3, gravitational
softening epsilon=12.5 kpc/h). The runs produced 15 outputs since the initial redshift (z=60).
Non-Gaussianity is parametrized by the f_NL parameter and there are 7 simulations of Box1 (with values of
f_nl = 0, (+/-)100, (+/-)500 and (+/-)1000) and 5 simulations of Box2 (with values off_nl = 0, (+/-)100 and
(+/-)200. Recently there are also some simulations performed utilizing g_nl. Box2 simulations where performed
at HRLB2 at LRZ under the project h0073.
The project Wiki (restricted).
Name explanation Lando. |
| Baryons in non- gaussian simulations | |
 |
Bings
correspond to Box2 from the Name explanation Bings. |
| Young Objects with Dark energy | |
 |
Yoda is a numeriocal simulation in the framework
of a cosmological model with dark energy. The aim is to study primordial gas clouds
which are likely to host the first stars. The presence of dark energy with an equation
of state w < -1 can significantly change the formation time of these first objects and
therefore the time of reoization of the Universe will change.
Name explanation Yoda. |